
- RFQ
- BOM
-
Contact Us
Tel: +86-0755-83501315
Email: sales@sic-components.com
- Chinese
- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
What is a thermocouple and its function?
A thermocouple is a fundamental temperature - sensing device that has been integral to scientific research, industrial processes, and everyday technology for over two centuries. Its simplicity, durability, and wide temperature range make it one of the most widely used temperature sensors in the world. This article delves into the working principles, key functions, and diverse applications of thermocouples, highlighting their significance in modern technology.
1. The Fundamental Principle of Thermocouples
1.1 The Seebeck Effect: The Core Mechanism
A thermocouple operates based on the Seebeck Effect, discovered by Thomas Johann Seebeck in 1821. This effect states that when two different conductive materials (typically metals or alloys) are joined at two junctions, a small voltage (electromotive force, EMF) is generated if the two junctions are at different temperatures. The magnitude of this voltage is dependent on the temperature difference and the specific materials used.
Key Components:
Hot Junction (Measuring Junction): Exposed to the temperature being measured.
Cold Junction (Reference Junction): Maintained at a known constant temperature (often ambient or 0°C) for reference.
Voltage - Temperature Relationship: The EMF generated is approximately linear over a specific temperature range but varies with different material combinations. For example, a Type K thermocouple (chromel - alumel) produces about 41 μV/°C at room temperature.
1.2 Material Combinations and Standard Types
Thermocouples are classified into standardized types based on their material pairs, each optimized for specific temperature ranges and environmental conditions:
Type Materials Temperature Range Key Characteristics
K Chromel - Alumel -200°C to +1350°C Cost - effective, widely used in industrial applications; good resistance to oxidation.
J Iron - Constantan -210°C to +760°C Suitable for dry environments; limited use above 500°C due to iron oxidation.
T Copper - Constantan -270°C to +400°C Excellent accuracy at low temperatures; ideal for cryogenics and food processing.
E Chromel - Constantan -270°C to +1000°C Highest output voltage among standard types; suitable for high - humidity environments.
R/S Platinum - Rhodium alloys 0°C to +1768°C High - temperature resistance; used in furnaces and calibrations; expensive.
B Platinum - Rhodium alloys 50°C to +1820°C Low EMF at room temperature; ideal for extremely high - temperature measurements.
2. Key Functions of Thermocouples
2.1 Temperature Measurement: The Primary Role
The primary function of a thermocouple is to convert temperature differences into an electrical signal, enabling precise and real - time temperature monitoring:
Direct Temperature Sensing: By placing the hot junction in the environment to be measured (e.g., a furnace, engine, or chemical reactor), the thermocouple generates an EMF proportional to the temperature. This signal can be read by a voltmeter or integrated into a data acquisition system.
Wide Range of Applications: Thermocouples can measure temperatures from cryogenic levels (e.g., liquid nitrogen at -196°C) to molten metals (e.g., Type B up to 1820°C), making them suitable for almost any industrial or scientific scenario.
2.2 Temperature Control in Industrial Processes
Thermocouples are critical for feedback control in systems that require precise temperature regulation:
Closed - Loop Control Systems: In a furnace, the thermocouple measures the actual temperature and sends the signal to a controller. The controller compares this to the setpoint and adjusts the heating element (e.g., turning it on/off or varying its power) to maintain the desired temperature.
Example: Chemical Reactors: In pharmaceutical or petrochemical plants, thermocouples ensure that reactions occur at optimal temperatures, preventing under - or over - heating that could compromise product quality or safety.
2.3 Safety and Alarm Systems
Thermocouples play a vital role in preventing equipment damage and ensuring safety by detecting abnormal temperature conditions:
Overheat Protection: In motors, transformers, or electronic devices, thermocouples monitor temperatures and trigger alarms or shut - off mechanisms if thresholds are exceeded. For example, in aircraft engines, thermocouples detect hot spots that could indicate mechanical failure.
Fire Detection: In commercial buildings, thermocouple arrays can identify temperature spikes early, enabling faster fire response than traditional smoke detectors in certain scenarios.
2.4 Calibration and Reference Standards
High - precision thermocouples (e.g., Types R, S, B) are used as reference standards in calibration laboratories:
Traceability to International Standards: By comparing an unknown sensor to a calibrated thermocouple, technicians can ensure the accuracy of other temperature - measuring devices (e.g., resistance thermometers or infrared sensors).
Primary Thermometry: While not as precise as primary thermometers (e.g., gas thermometers), thermocouples are often the practical choice for industrial calibration due to their durability and ease of use.
3. Design and Construction of Thermocouples
3.1 Junction Types
The design of the thermocouple junction affects its response time and durability:
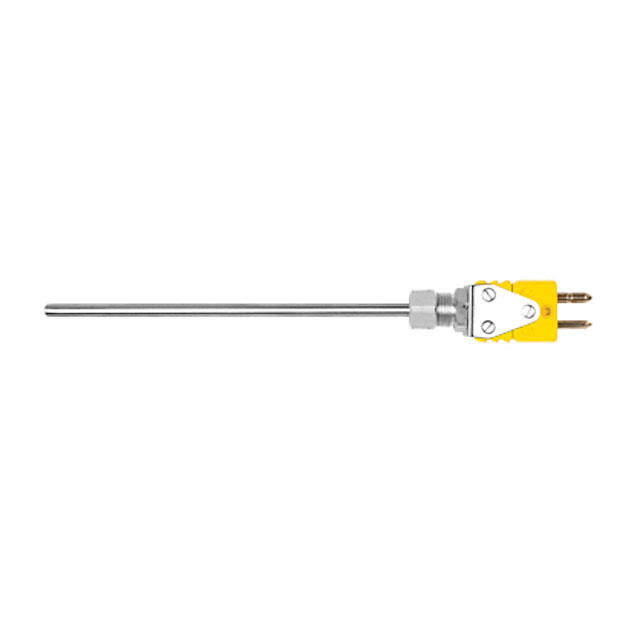
Bare - Wire Junction: The wires are welded together without protection, offering the fastest response time but limited protection from corrosion or mechanical damage. Suitable for laboratory or clean environments.
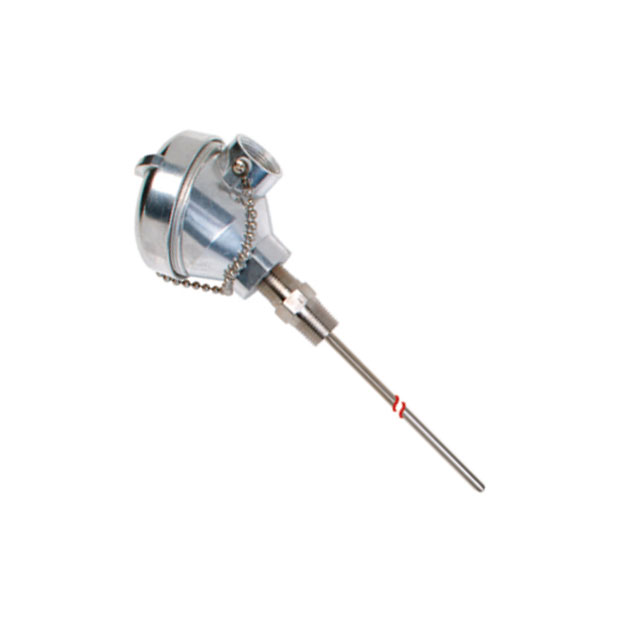
Sheathed Junction: Encased in a metal tube (e.g., stainless steel) with mineral insulation (e.g., magnesium oxide), this type is rugged and resistant to moisture, chemicals, and vibration. Commonly used in industrial settings.
Grounded vs. Ungrounded Junctions:
Grounded: The junction is welded to the sheath, providing good thermal conductivity but potential electrical interference.
Ungrounded: The junction is isolated from the sheath, reducing interference but with slightly slower response.
3.2 Signal Conditioning and Compensation
To convert the thermocouple's EMF into a usable temperature reading, additional components are required:
Cold Junction Compensation (CJC): Since the EMF depends on the cold junction temperature, a CJC circuit (e.g., using a thermistor or integrated circuit) measures the ambient temperature of the cold junction and adjusts the reading accordingly.
Amplification and Transmission: The low - level EMF (μV range) is amplified and may be converted to a standard signal (e.g., 4 - 20 mA or digital data) for transmission to a display or controller.
Shielded Cables: To minimize electromagnetic interference, thermocouple wires are often enclosed in shielded cables, especially in noisy industrial environments.
4. Applications of Thermocouples
4.1 Industrial Manufacturing
Metallurgy: Measuring temperatures in foundries during metal casting, heat treatment (e.g., annealing, quenching), and welding processes. Type K thermocouples are commonly used here due to their high - temperature resistance.
Food Processing: Ensuring proper pasteurization, sterilization, and cooking temperatures. Type T thermocouples are ideal for their accuracy in low - to - medium temperatures.
Power Generation: Monitoring turbine temperatures in power plants, exhaust gases in boilers, and transformer oil temperatures.
4.2 Aerospace and Automotive Sectors
Aerospace: Measuring engine combustion temperatures, cabin environmental control systems, and thermal protection system performance during re - entry.
Automotive: Engine temperature monitoring, exhaust gas temperature sensing for emission control, and battery thermal management in electric vehicles.
4.3 Scientific Research and Laboratories
Material Science: Studying phase transitions (e.g., melting, boiling) and thermal properties of materials.
Cryogenics: Measuring temperatures in liquid nitrogen (-196°C) or helium (-269°C) environments using Type T or K thermocouples.
Environmental Research: Monitoring soil and air temperatures in climate studies or volcanic activity.
4.4 Consumer and Medical Devices
Home Appliances: Ovens, water heaters, and air conditioners use thermocouples for temperature control.
Medical Equipment: Monitoring patient body temperature, sterilization autoclaves, and hyperthermia treatment systems.
5. Advantages and Limitations of Thermocouples
Advantages
Wide Temperature Range: From cryogenic to extremely high temperatures, few sensors match thermocouples' versatility.
Durability: Sheathed types can withstand harsh environments (corrosion, vibration, high pressure).
Fast Response: Bare junctions react quickly to temperature changes, essential for dynamic systems.
Simple Design: No external power source needed; self - generating EMF simplifies installation.
Cost - Effective: Especially for high - temperature applications, thermocouples are cheaper than alternatives like resistance thermometers.
Limitations
Low Output Voltage: Requires amplification, increasing complexity and potential for noise.
Non - Linear Response: EMF vs. temperature is not perfectly linear, requiring calibration or linearization circuits.
Cold Junction Compensation: Necessary for accuracy, adding to system complexity.
Drift over Time: Repeated heating and cooling can cause material degradation, affecting accuracy; periodic recalibration is recommended.
6. Future Trends and Innovations
Miniaturization: Micro - thermocouples integrated into MEMS (micro - electromechanical systems) for precise temperature sensing in microchips or medical implants.
Smart Thermocouples: Embedded with IoT capabilities for wireless data transmission and self - diagnostics.
High - Temperature Materials: Development of new alloys for thermocouples to extend the upper temperature limit beyond 2000°C for aerospace and energy applications.
Calibration-Free Designs: Advanced materials and algorithms to reduce the need for frequent calibration, improving reliability in remote or inaccessible locations.
Conclusion
Thermocouples, with their roots in 19th - century physics, remain indispensable in modern technology due to their simplicity, durability, and wide applicability. From regulating furnace temperatures in steel mills to monitoring engine health in aircraft, their ability to convert thermal energy into electrical signals has shaped countless industries. As technology evolves, thermocouples continue to adapt, combining with digital systems and advanced materials to meet the demands of next - generation temperature sensing. Their legacy as a cornerstone of thermal measurement is a testament to the enduring value of elegant scientific principles in practical engineering solutions.
https://www.sic-components.com/sensors-transducers
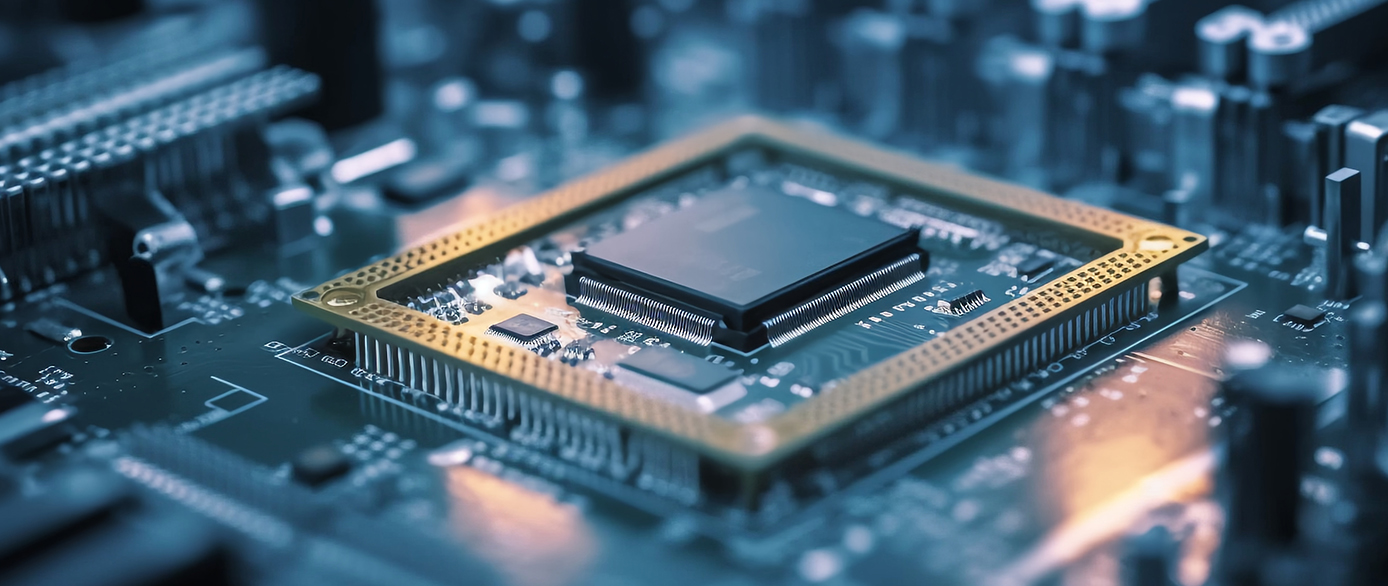
Hot Products
View MoreRelated Blogs

2000+
Daily average RFQ Volume

30,000,000
Standard Product Unit

2800+
Worldwide Manufacturers

15,000 m2
In-stock Warehouse













 Wishlist (0 Items)
Wishlist (0 Items)